What are Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) or Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) materials?
INTRODUCTION
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), sometimes referred to as thermoplastic rubbers (TPR), are polymeric materials, which exhibit elasticity at ambient temperatures and can be processed as plastics by injection moulding. TPE exhibits properties of both rubber and plastic materials. Most thermoplastics including TPEs are not subjected to cross-linking, means they can be remelted and re-shaped. TPE offers elasticity benefits over a wide temperature range. It's rubber like properties have enabled TPE to replace rubber significantly in several applications. Products from TPEs can be processed by a number of processes like injection moulding, extrusion, rotational moulding, blow moulding. The target area for growth of TPEs is primarily in thermoset rubber replacement, new elastomeric application or soft thermoplastic replacement where, greater flexibility is demanded.

Advantages of Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE)
- TPEs have outstanding thermal properties and material stability when exposed to a broad range of temperatures
- Can be produced in a variety of hardness grades
- TPE requires little or no compounding, with no need to add reinforcing agents, stabilisers or cure systems.
- The possibility of reusing scrap in the same fashion as with thermoplastics.
- Excellent chemical and weather resistance
- TPEs are generally low-modulus, flexible materials that can be stretched repeatedly
- Very good electrical insulation properties
Disadvantages of TPE
- Poor high temperature performance. Melting at elevated temperatures restricts the use of TPE parts well below their melting point.
- Comparatively, higher cost than thermoset rubbers
- Limited number of low-hardness TPEs available compared to thermoset rubbers.
- Low resistance to aromatics
Applications of TPE
- Automotive: Suspension bushings, pressure pipes, Grommets, bumpers, Seals, air ducts, internal and external trims, shock absorber boots.
- Consumer products: refrigerator seals, vacuum cleaners parts, power tool handles and overmoulding, mobile phone covers, shock absorbing pads.
- Electrical and Electronics: Electrical cable jacket, mobile phone components, plugs and sockets, remote control covers
- Medical: ventilation masks, breathing tubes, syringe seals, seals, valves, catheters, ventilator parts.
- Construction: Ventilation, and air conditioning, door and window seals, glazing seals, pipe seals
- Footwear and sporting goods: Shoe soles, sporting goods, Ski equipments, diving flippers, snorkels.
What is Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
INTRODUCTION
Liquid Silicone Rubber is a low viscosity thermoset elastomer maintaining mechanical properties over a wide range of temperatures. Silicone rubber is a durable and highly-resistant elastomer (rubber-like material) composed of silicone (polymer) containing silicon together with other molecule like carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Due to the thermosetting nature of the material, liquid silicone injection moulding requires special treatment, such as intensive distributive mixing, while maintaining the material at a low temperature before it is pushed into the heated cavity and vulcanised. Silicone rubber is a high-performance elastomer characterised by an unusual combination of properties. These properties range from high temperature performance to durability.

Characteristics of Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
- Liquid Silicone Rubber parts are durable and can withstand extreme temperatures
- Excellent non-stick and non-adhesive properties
- Liquid silicone rubber resists water, oxidation and some chemicals such as acids and alkali
- LSR has good elongation, high tear and tensile strength, excellent flexibility
- Compared to other elastomers, silicone can withstand a wide range of high/low temperature extremes
- Excellent insulation properties, low toxicity, tasteless and odourless
Applications of Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
- Automotive industry specially under the hood components, sealants, gaskets, connectors, radiator components, heat exchangers, engine covers, valve covers.
- Medical and Healthcare products, LSR is popular material in medical industry due to excellent biocompatibility, seals, gaskets, o-rings, tubing, drainage, valves, membranes, respiratory care, masks, medical instruments, medical cables, baby bottle nipples.
- Electrical and Electronic components, , connectors, insulators, gaskets, lighting applications such as diffusers, floodlighting etc.
- Consumer Products like kitchen cookware, food utensils, baking pans, spatulas, packaging equipment:
- Swimming goggles, snorkels, mouthpieces for players.
Snapshot of Injection Moulding process
- Once Moulds are ready for production, then injection moulding process itself is highly efficient and cost-effective.
- Injection moulding is ideal for high volume production of plastic moulded parts. High production output makes the moulding process cost-effective.
- Multiple types of plastics can be simultaneously used from a single mould.
- Consistent quality output achieved by repeatedly using the same mould for each component.
- Injection moulding can provide the desired finish even multiple finishes on the same part can be easily achieved.
- Plastic injection moulding is a sustainable process means waste can be easily recycled.
- Wide variety of moulding materials available ranging from opaque, transparent, translucent finish.
- Complex and intricate parts can easily be designed and manufactured by injection moulding process.
- Automotive Components: Dashboards, grilles, central console, cup holders, bumpers, head and tail light housings, reflectors made by the injection moulding process.
- Medical and Healthcare: Medical and surgical devices, orthopaedic devices, hearing aids, inhalation masks, ventilator, Medication Trays.
- Electrical and Electronic components are commonly moulded with injection moulding process such as housings, Phones, enclosures, remote controls, computers, TV sets, printer housings, drone parts.
- Packaging: Food and Beverage packaging, Personal care and cosmetic packaging, Consumer packaged goods, Healthcare and Pharmaceutical packaging, Household and chemical Packaging
- Agriculture and Farming: Irrigation products, Pipes, Tractor parts, farming machinery parts, sprinklers, water tanks.
- Building and Construction: Windows and doors, Hardware items, Fixtures, power-tool housings, cladding panels, Pipe and Gutters, plumbing parts, Bath and showers.
- Packaging: Food and Beverage packaging, Personal care and cosmetic packaging, Consumer packaged goods, Healthcare and Pharmaceutical packaging, Household and chemical Packaging
- Household, Leisure and Sports goods, Furniture, Home appliances, vacuum cleaner, Luggage items, Vending Machine components, toys like Lego blocks, POP (Point of Purchase) display racks.
- Not economical for low volume production due to higher initial tooling cost.
- Plastic parts need to be designed by following set rules for injection moulding. Like complex undercuts, variable wall sections could be challenging.
- Lead time is higher due to initial tooling preparation.

How Injection Moulding process works
INTRODUCTION
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process used for producing parts by injecting molten resin into a mould. Most of the mass-produced plastic items are made by injection moulding process. Injection moulding is a very adaptable process used for moulding a wide range of thermoplastic materials and finishes, which makes it a popular option in numerous industries like automotive, aerospace, electrical, electronics, transportation, medical and healthcare.Firstly custom-made moulds are prepared, Tool steel is common material for preparing the moulds however aluminium or 3d-printed moulds can be used for short-run production. These moulds are mounted on a moulding machine and injected with a raw material which shapes the polymer into the desired form, creating identical copies of the same part.
INJECTION MOULDING MACHINE OVERVIEW
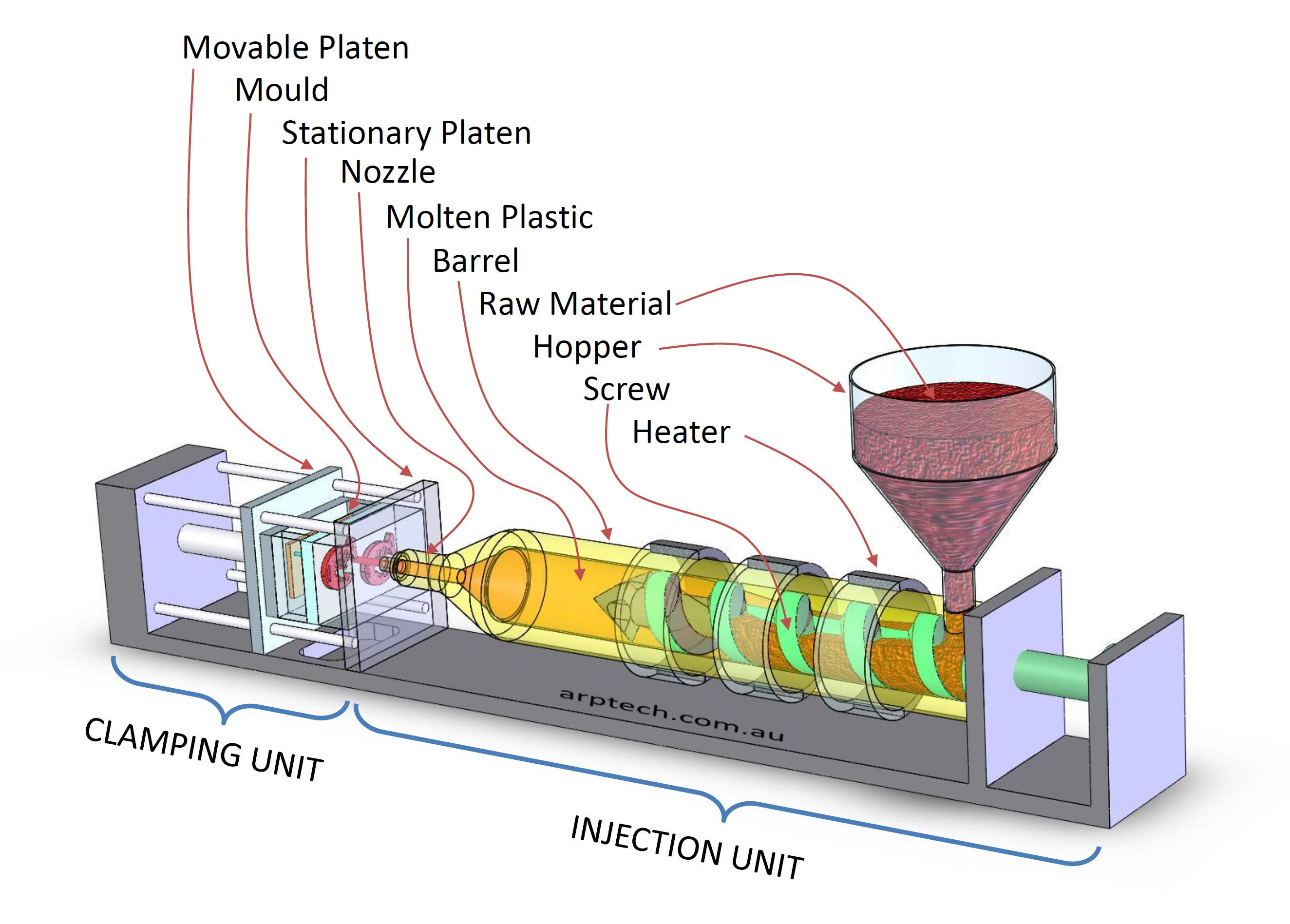
PROCESS STEPS
The injection moulding process uses a special purpose machine consisting of three main parts: the injection unit, the mould and the clamping unit. Firstly plastic granules are loaded from a hopper into a spinning auger. These granules are passed through a heated chamber, called barrel where plastic is melted and injected into a mould with high pressure using plunger. The moving part of the mould is forced against the fixed part by a hydraulic ram with several tonnes of force. The plastic enters the mould cavity through a gate and runner system. After the cavity is filled, the mould is held closed during plastic injection and cooling cycle until plastic solidifies. At this time the auger screw and barrel retracts to its original position to get ready for the next cycle. Once the moulded part cools down completely, the mould is forced to open by the hydraulic ram and the moulded item is ejected out for further processing. The next injection moulding cycle repeats as soon as the mould closes and the plastic is injected into the mould cavity.