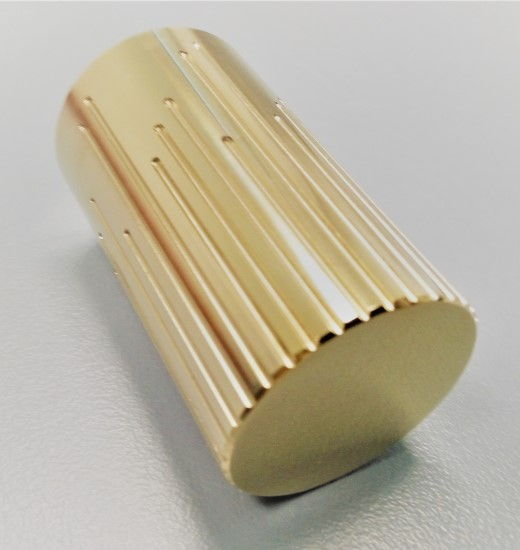
Snapshot of Brass
Brass Description
Brass has long been a popular material for decoration for its bright gold-like appearance. The most commonly used colour of brass is bright golden. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve varying mechanical and electrical properties. Brass is commonly used in applications where low friction and corrosion resistance is required. Brass components can often be used without any extra surface protection.
Advantages of Brass parts
Brass is a good conductor of heat, making it a first choice for heat exchangers (radiators). Brass has desirable acoustic properties appropriate for use in musical instruments. Brass is not ferromagnetic. Brass is durable and hygienic making it suitable for frequently touched surfaces. Brass is easy to machine.
Brass Uses
Musical instruments, locks and door handles, electronic components, plumbing hardware, valves, heat exchangers, Gears, electrical components.
Finishing examples of Brass prototypes
Available Finishes
- Machine finish
- Polished finish
- Mirror polished finish
- Bead blast finish (to give satin texture)
- Chrome Plating
Brass material Spec
| Property | Data |
|---|---|
Density
|
8.60 g/cm3 |
Tensile Strength (Mpa)
|
360 Mpa |
Modulus of Elasticity (GPa)
|
106 GPa |
Thermal Conductivity (k)
|
120 W/m-K |
Melting Point (℃)
|
915℃ |
Note: This Data is indicative only
|
|
Further considerations
Brass does not become brittle at low temperatures like mild steel. Brass products can often be used without needing extra surface protection.
Limitations
Brass is susceptible to stress corrosion cracking, poor impact resistance, prone to tarnish with time.