3DP (3D Printing) Process Explained
What is 3DP - 3D Printing:
3D printing is a layered manufacturing process used for building a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. "3D printing" is a generic term used for variety of additive manufacturing processes in which material is deposited layer-by-layer, joined or solidified under the controlled conditions. 3D printing and additive manufacturing reflect that the technologies share the theme of material addition or joining throughout a 3D work envelope under automated control. These deposited materials range from molten resins, liquids or powder grains fused together, typically layer by layer. The 3d printing technology is commonly applied on initial conceptual designs. In addition, parts can be used for form fit and light testing purpose.

How 3D-Printing works:
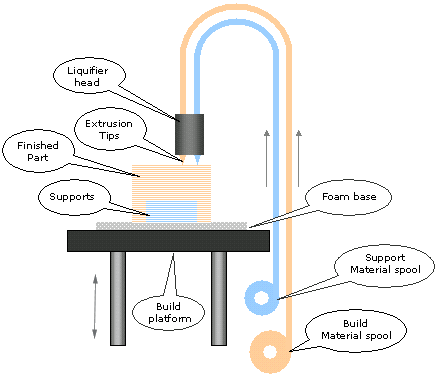
3d printing process, based on FDM technology, starts with a 3D CAD model sliced into thin layers in Z-axis. These sliced layers are used to drive an extrusion head of 3d printing machine. The building material, in the form of a thin solid filament, is fed from a spool to a movable head controlled by servo motors. Second filament is fed from adjacent nozzle for support material, used to give support for overhanged or cantilever features. The filament reaches the liquifier head, melts it and then extruded through a nozzle onto the part surface. After covering the whole cross section build platform descends by one layer thickness to lay down the next layer. Process repeats itself until full 3D part is formed. The temperature of machine chamber is precisely controlled below the melting point of the material so that only little amount of heat is required to melt the filament and on the other hand part need to be kept cool enough so that the molten material solidifies upon contact. There's wide range of FDM based 3d printing materials available like, PLA, ABS, Nylon, PET, PETG, TPU, ASA, PC etc. However PLA (Polylactic Acid) is very popular as it's biodegradable, inexpensive and easy to work with.
FDM based 3D Printing process overview
Advantages of 3DP Process
- Cost effective solution for small to medium size parts in shortest lead time
- Parts are dimensionally stable and make them suitable for form, fit and functional testing
- Some 3d printed materials are stable under harsh environmental exposure.
- Ideal for strong parts exposed to temperature, water and many chemicals.
- High level of finish can be achieved by sanding and other post processing techniques.
- 3d printed parts can be further machined, tapped, polished or painted.
Limitations of 3DP Process
- Parts have a ribbed appearance due to layering process
- Extensive snap and living hinge features could fail due to process and material limitations.
- 3DP could be a slower process for very large build volume parts subject to part complexity and shape. Thin wall and hollow parts are faster to make than solid builds.
General Applications of 3DP parts
- Conceptual models for effectively evaluating, optimising and communicating your design
- End use products without spending on tooling, moulding and machining
- 3DP parts can be directly used for tools such as Jigs and fixtures, production or tooling
- Excellent choice for extrusion profile verification
- Product designers use 3DP parts for form, fit and function analysis and concept visualisation
- Medical, Healthcare and Defence industries use 3DP products for form, fit and functional analysis
- Consumer and Educational industries have great demand of 3D printed conceptual or visual parts due to quick turnaround
Use 3D Printed parts for:
- Concept models for initial stage of prototyping.
- When material requirement is not so critical.
- Form, Fit and Function analysis of prototypes
- Short run production of small to medium size parts

