3D Printing using SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) Process
What is SLS 3D Printing
SLS also known as Selective Laser Sintering, primarily used to quickly produce three-dimensional parts, layer by layer, from powdered materials. The CO2 Laser provides a concentrated heating which welds (sinters) the powder within a precisely controlled chamber. SLS has the distinctive advantage of having the wide variety of materials that can be suitable for functional analysis.
How SLS works:
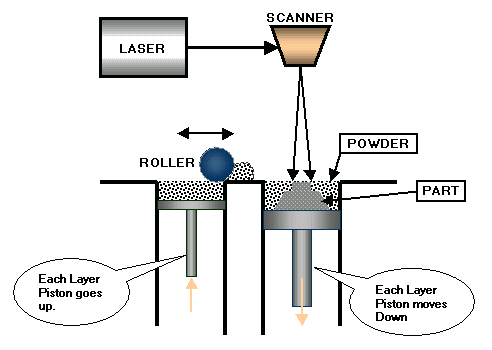
SLS process produces parts directly from 3D CAD model; layer by layer similar to SLA but rather than liquid resin, powder is used. The CO2 Laser provides a concentrated heating beam which is traced over the tightly compacted layer of fine heat-fusible powder. The temperature in the entire chamber is maintained little below the melting point of the powder. So the laser slightly raises the temperature to cause sintering, means welding without melting. For the next level, the piston moves down along with the formed object and powder is spread with a roller for the next layer. Process repeats until the full object is formed. Functional products with snap fits, living hinges, thermally and mechanically loaded parts. SLS has a wide variety of materials available. SLS polyamide (Nylon) material allows the production of fully functional prototypes with high strength and suitable for snap fits, living hinges features. SLS (GF) Glass Filled Nylon is suitable for high thermal resistance and high impact strength prototypes. SLS Somos is used for functional rubber like parts.
SLS MACHINE OVERVIEW
Advantages of SLS Process
- The SLS polyamide (Nylon) material allows the production of fully functional prototypes with high mechanical and thermal resistance and suitable for snap fits, living hinges features.
- Glass filled Nylon is suitable for functional applications that require strength & rigidity under the extreme conditions of high temperature or chemical agents.
- Rubber like flexible parts can be directly made using elastomer polymer Somos 201, shore A hardness 75, suitable for seals, gaskets & high temperature applications.
- Durable metal parts and mould inserts direct from CAD model using ST200 similar to P20 steel.
- Low density complex investment casting patterns - directly from CAD files using Cast form PS.
Limitations of SLS Process
- Typical SLS parts have little rough grainy & porous surface finish which is not as smooth as SLA but acceptable for most applications, but parts can be easily primed and finished to the smooth level.
- The larger shrink rates of SLS increase the tendency for the prototype to warp, bow or curl subject to the part geometry.
- SLS features detail is not as crispy and sharp as produced by SLA.
General Applications of SLS parts
- Conceptual models for effectively evaluating, optimising and communicating your design.
- End use products without spending on tooling, moulding and machining.
- Functional SLS parts allow you to test in real world environments.
- SLS parts can be directly used for manufacturing Automotive, Aerospace and Engineering components
Use SLS for:
- Functional prototypes with high mechanical and thermal resistance
- Ability to easily make very complex geometries directly from digital CAD data.
- Functional applications that require strength and rigidity under the extreme conditions
- For conceptual and functional models.

